Description
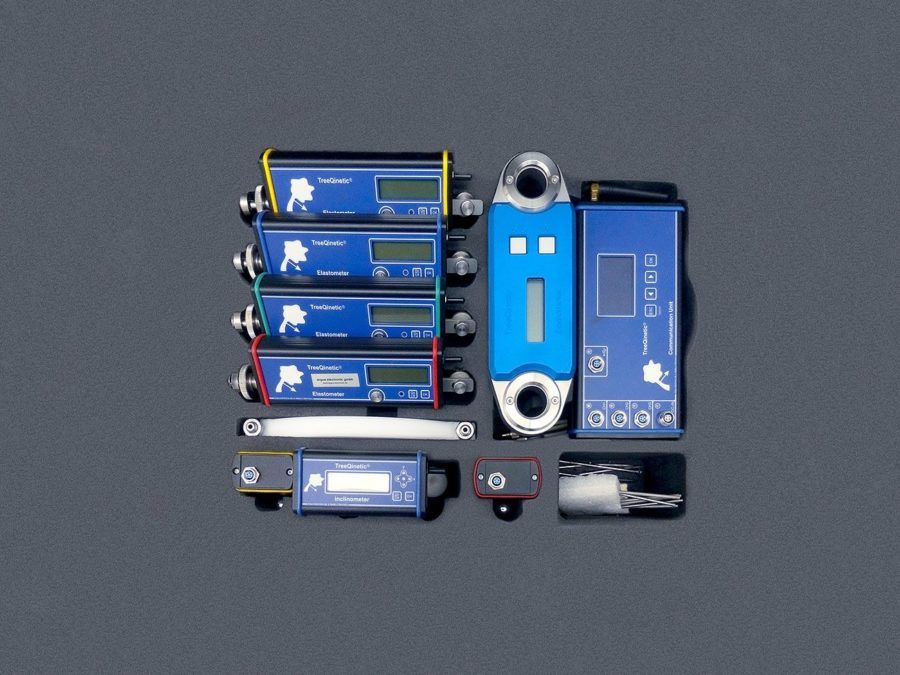
PiCUS TreeTronic Description
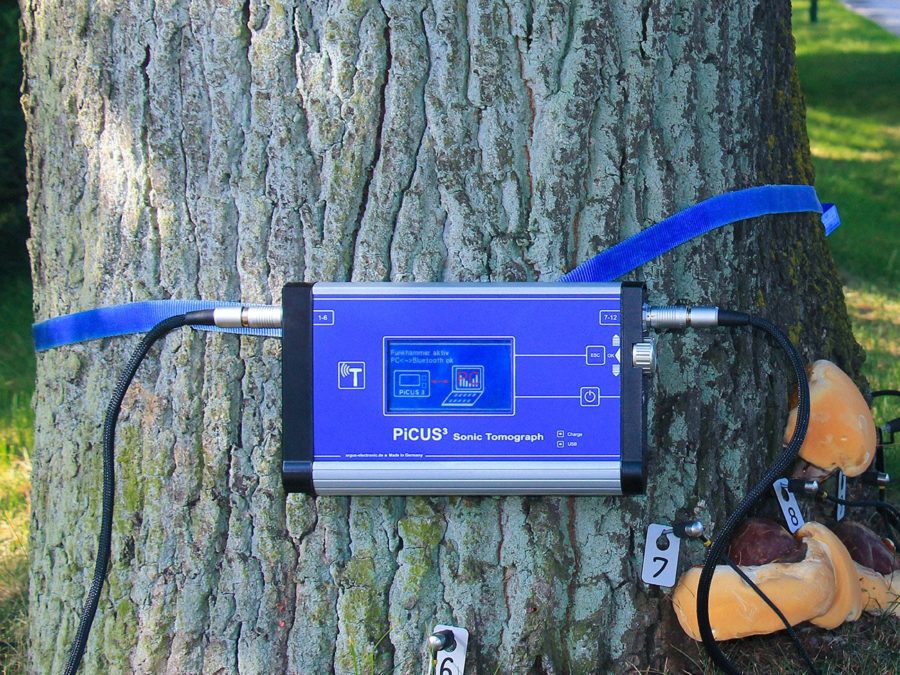
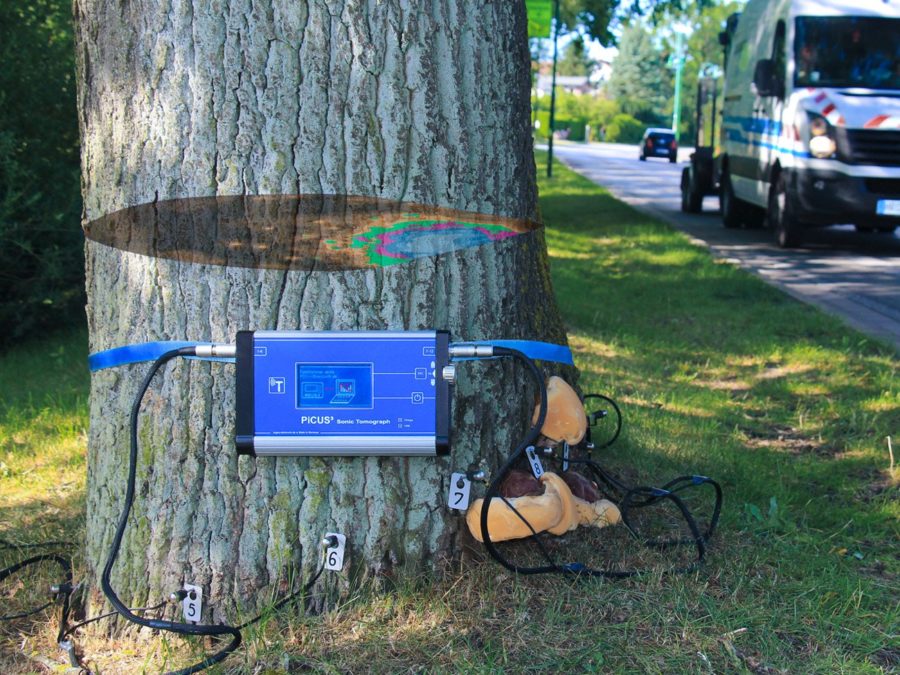
The electrical resistance tomograph PiCUS TreeTronic is used for detailed tree examinations as part of road safety inspections in combination with the PiCUS Sonic Tomograph in order to determine more precisely the remaining wall thickness as well as more detailed information about the type and extent of damage. The electrical resistance tomography of the PiCUS TreeTronic show in particular the early stages of rot and help to interpret sonic tomograms if they provide blurred images due to cracks in the tree. The measurement method is abbreviated with the letters ERT (Electric Resistance Tomography).
The measurement results of the electrical resistance tomograph (ERT) can be displayed in 2D and 3D graphics using the PiCUS Expert software. This shows the extent of the defect in gradations. The 3D view also shows the vertical course of the damage. This data can be used to make a forecast of how the tree’s resistance to breakage will develop over the next few years.
PiCUS TreeTronic functional scope:
Measuring channels: Up to 24 measuring points per measurement possible (even number required)
Tree circumference: Tree circumference: up to about 6.5 meters
Operation: Possible with or without a PC, the integrated control computer stores over 100 measurements
Connection: PC connection via Bluetooth for analyzing the measurement results and GPS for determining the position of the tree
Measuring principle
The measuring principle:
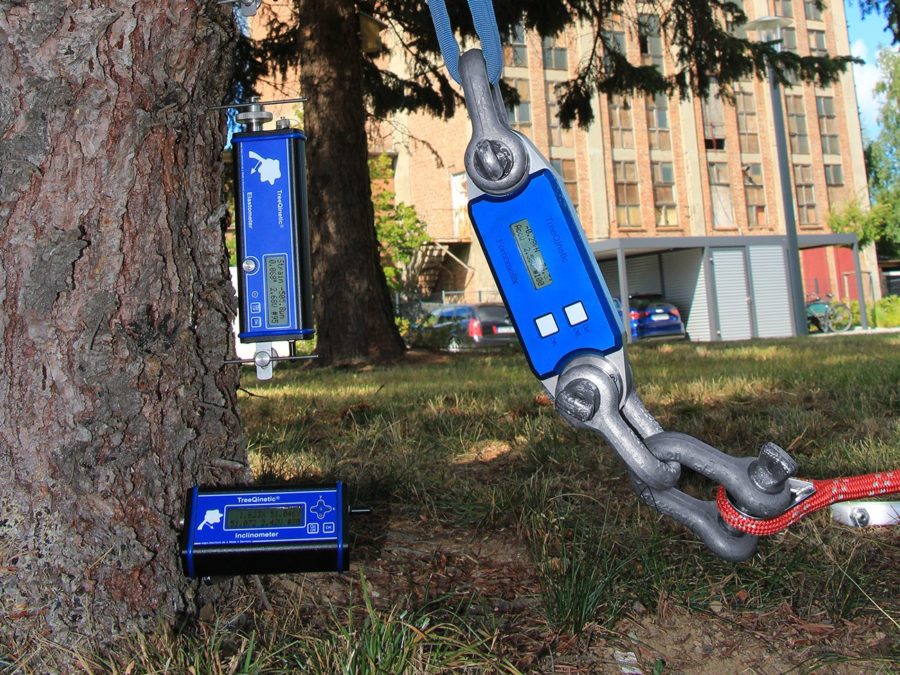
The PiCUS TreeTronic analyzes the condition of the wood of a tree with the help of measurements of the electrical resistance of the wood. The electrical resistance of the wood is essentially influenced by the water content and the ions dissolved in the water. Rots often have a high level of moisture and therefore low resistance. In addition, the chemical composition of the wood and the cell structure influence the resistance. Propagation of the electrical field During a measurement, the TreeTronic device couples electrical voltages of up to 100 volts to the measuring points and measures the resulting electrical field. Taking into account the geometry information of the measuring plane, a complex software calculates the apparent electrical resistances in the area of the measuring plane. These resistances are shown in a colored tomogram. By overlaying PiCUS sonic tomograms with electrical resistance tomograms, in many cases the remaining wall thickness can be determined more precisely for the purpose of assessing the fracture safety. Unlike sonic tomography, ERT suffers less from cracks in the trunk, so the TreeTronic tomograms often help to interpret the sonic tomograms correctly.
Technical details
Technical details
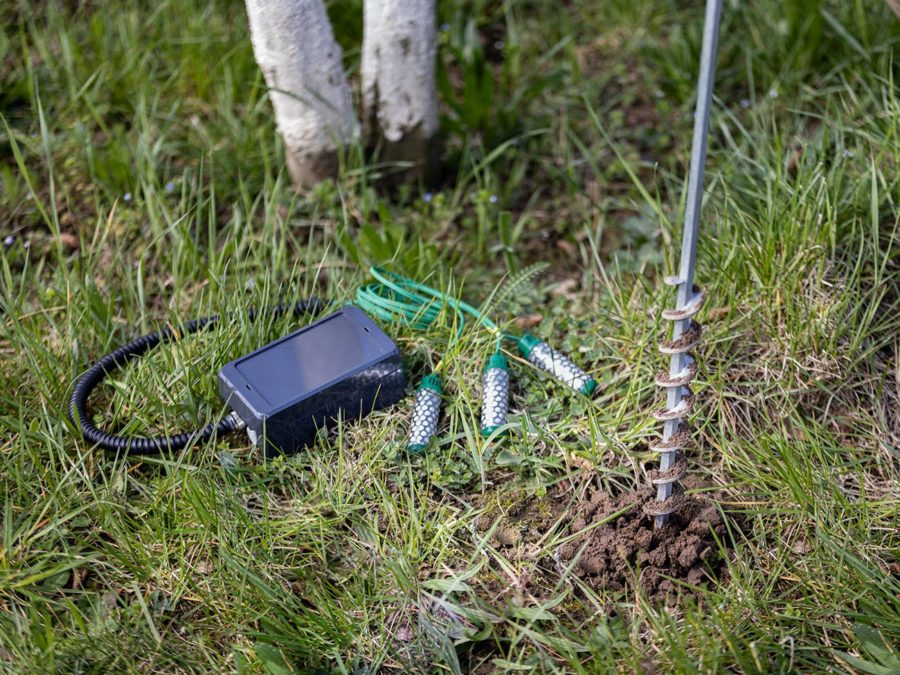
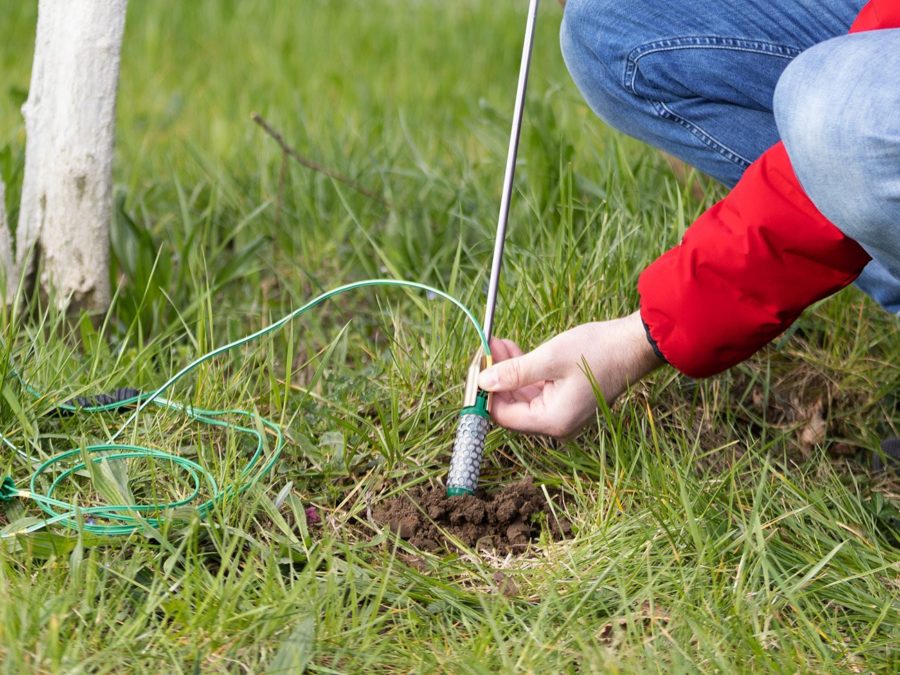
The PiCUS TreeTronic Tomograph is equipped with 24 measuring channels. The more of these channels are used, the more accurate the ERT is. Thin metal pins are required for coupling to the electrically conductive layers of the tree. For example nails, as they are also used for sound examinations, or pins when it comes to reducing the risk of damage.
| Girth of the tree: |
up to about 6.5 m |
| Number of measuring channels (= number of measuring points): |
even numbers up to 24 |













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.